Introduction to NumPy
MScAS 2025 - DSAS Lecture 2
2025-09-30
Why NumPy?
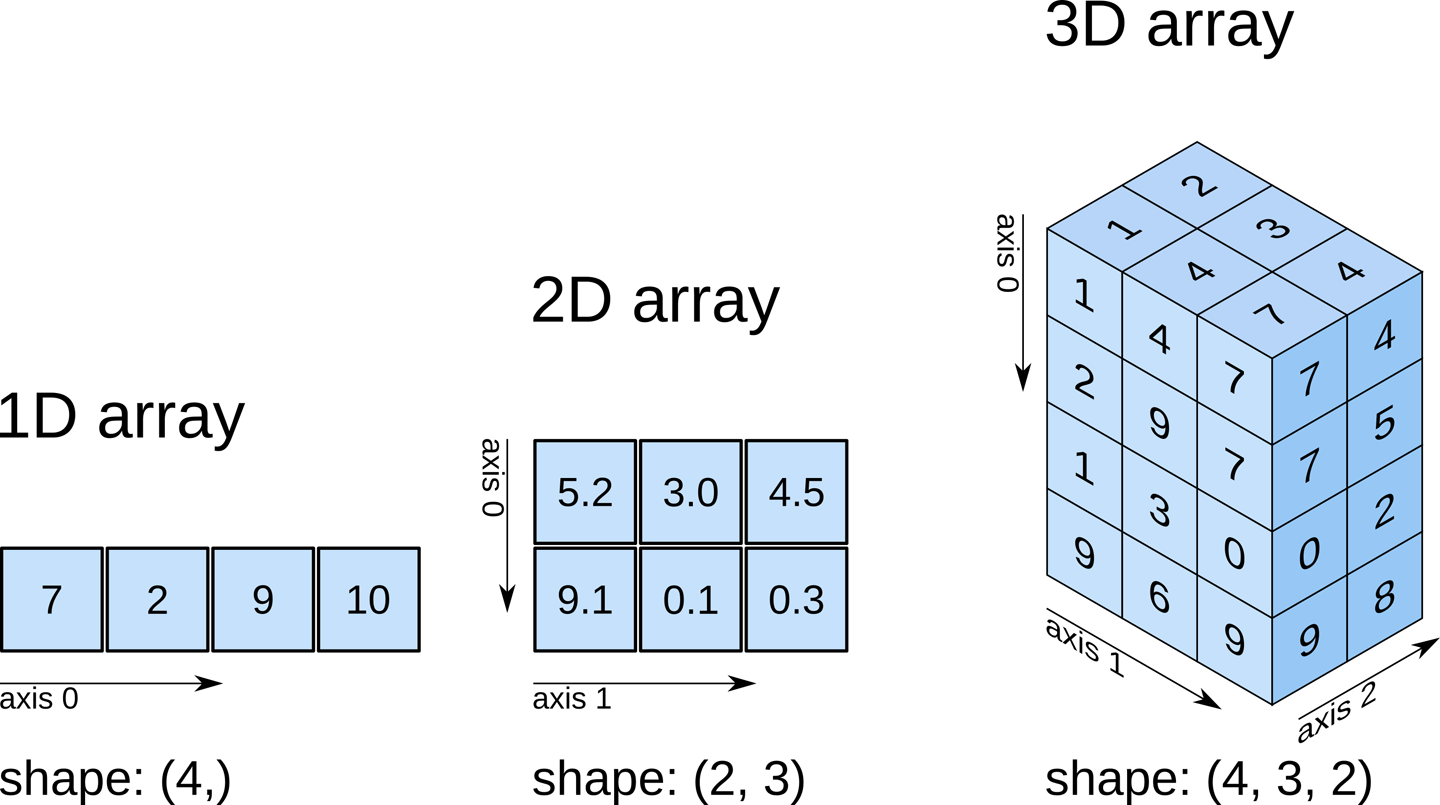
Array Basics
Note
Unlike Python lists, arrays contain elements of the same data type.
arange vs linspace
np.arange(start, stop, step): Creates values with fixed step size- Example:
arange(0, 20, 5)→[0, 5, 10, 15](stops before 20) - Like Python’s
range(), endpoint is excluded
- Example:
np.linspace(start, stop, num): Creates num evenly spaced values- Example:
linspace(0, 10, 5)→[0.0, 2.5, 5.0, 7.5, 10.0](includes 10) - Endpoint is included by default
- Use when you need a specific number of points
- Example:
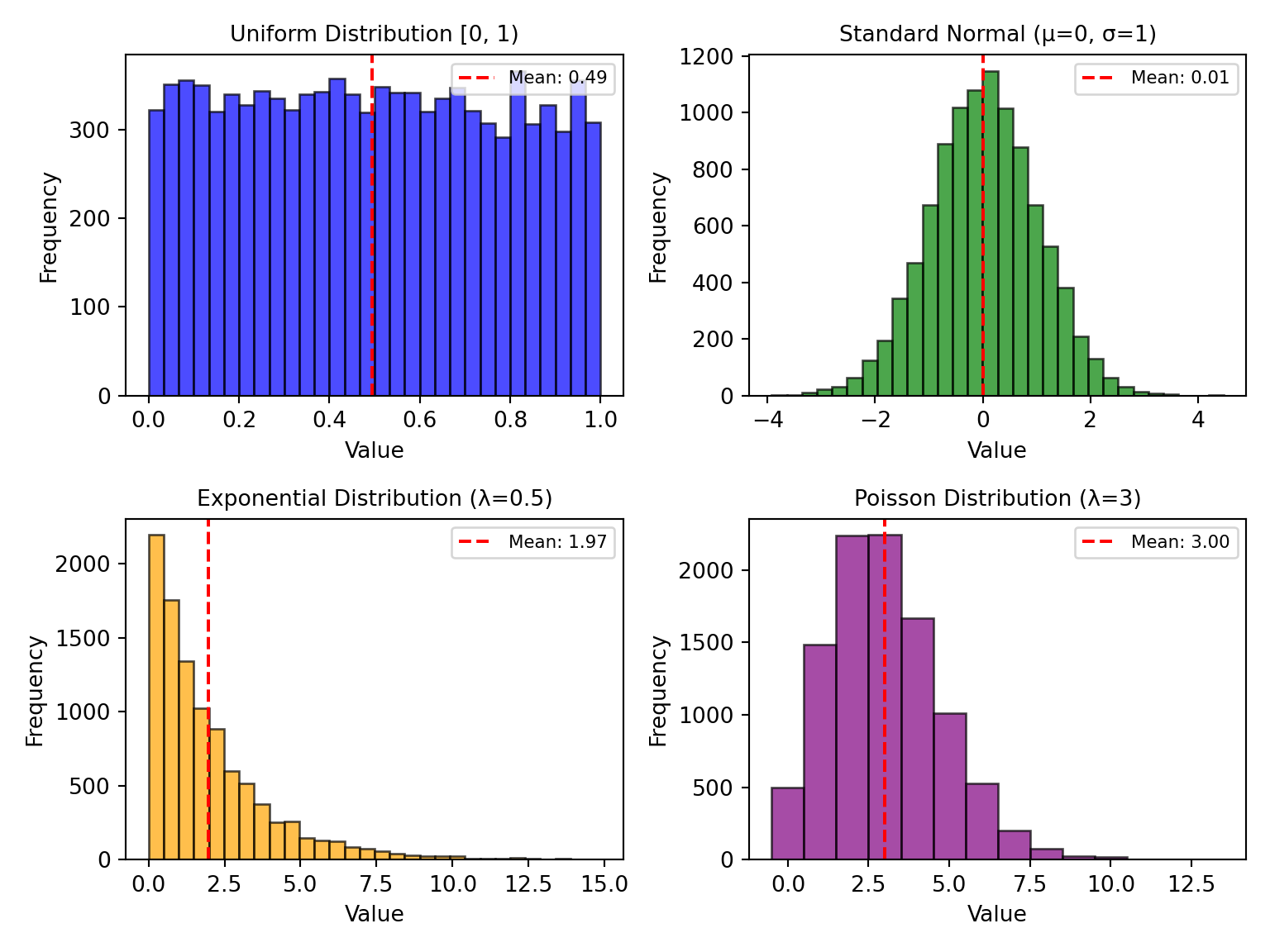
Reminder on Distributions
- Uniform: All values equally likely (dice rolls, random sampling)
- Normal: Bell curve, most common in nature (heights, measurement errors)
- Exponential: Time between events (Exp(scale = 1/λ), e.g. insurance claim arrivals, If a policyholder files 0.2 claims per year on average → λ = 0.2, mean time between claims = 5 years)
- Poisson: Count of events in fixed time (Pois(𝜆), e.g. number of claims per month, if 10 expected claims per month across a portfolio → λ = 10)
Why Random Numbers?
Random number generation has many usages. E.g. Monte Carlo simulations in risk assessment, Bootstrapping for confidence intervals, Synthetic data generation for testing, etc.
Interval Notation Explained
The notation [0, 1) uses mathematical interval notation:
[(square bracket) = inclusive (includes the value))(parenthesis) = exclusive (excludes the value)- Example:
[0, 1)means: 0 ≤ x < 1 (includes 0, excludes 1)
🤔 Pop Quiz
Which of the following is true?
- Arrays can contain elements of different data types
- Arrays can only contain elements of the same data type
- Arrays can only contain integers
- Arrays can only contain floats
Array Attributes
Array Attributes
The attributes of a numpy array are:
ndim: number of dimensions (axes) of an array.shape: tuple containing the size of an array in each dimension.size: total number of elements in an array.dtype: gives the data type of the elements of an array.itemsize: provides the size (in bytes) of the elements of an array.
Key Differences
For an array with shape (3, 4) and dtype int64:
shape = (3, 4)→ Structure: 3 rows × 4 columnssize = 12→ Total elements: 3 × 4 = 12 valuesitemsize = 8→ Each element occupies 8 bytes (int64)- Total memory:
size × itemsize = 12 × 8 = 96 bytes
🤔 Pop Quiz
For an array with shape (2, 3, 4), what is the total size?
- 9 elements
- 10 elements
- 24 elements (2 × 3 × 4)
- 234 elements
Indexing and Slicing
Note
Indexing and slicing are similar to Python lists but extended to multiple dimensions. Again, remember that indexing in Python starts at 0.
Warning
Arrays are mutable. meaning that changes modify the original (remember to use .copy() when needed!).
🤔 Pop Quiz
For a 2D array arr, what does arr[:, 1] select?
- The first row
- The second column (index 1)
- The first column
- A single element
Reshaping and Combining
Idea
How can we rearrange data without changing values?
🤔 Pop Quiz
Can you reshape an array of size 12 into shape (3, 5)?
- Yes, NumPy will pad with zeros
- Yes, NumPy will truncate extra elements
- No, 3 × 5 = 15 ≠ 12
- Yes, using -1 as a dimension
Vectorized Operations
| Operator | NumPy Function | Description |
|---|---|---|
+ |
np.add |
Addition |
- |
np.subtract |
Subtraction |
* |
np.multiply |
Multiplication |
/ |
np.divide |
Division |
** |
np.power |
Exponentiation |
% |
np.mod |
Modulus |
🤔 Pop Quiz
What does np.array([1, 2, 3]) * 2 produce?
- An error
- array([2, 4, 6])
- array([1, 2, 3, 1, 2, 3])
- 12
Aggregations
Idea
Aggregations are often used for summarizing data and doing some statstical analysis.
How
You must specify the axis along which the aggregate is computed
Claim Severity Analysis
Using gamma distribution to model claim amounts (common in actuarial practice)
🤔 Pop Quiz
For array [[1, 2], [3, 4]], what is arr.sum(axis=0)?
- array([4, 6])
- array([3, 7])
- 10 - total sum
- array([[4], [6]])
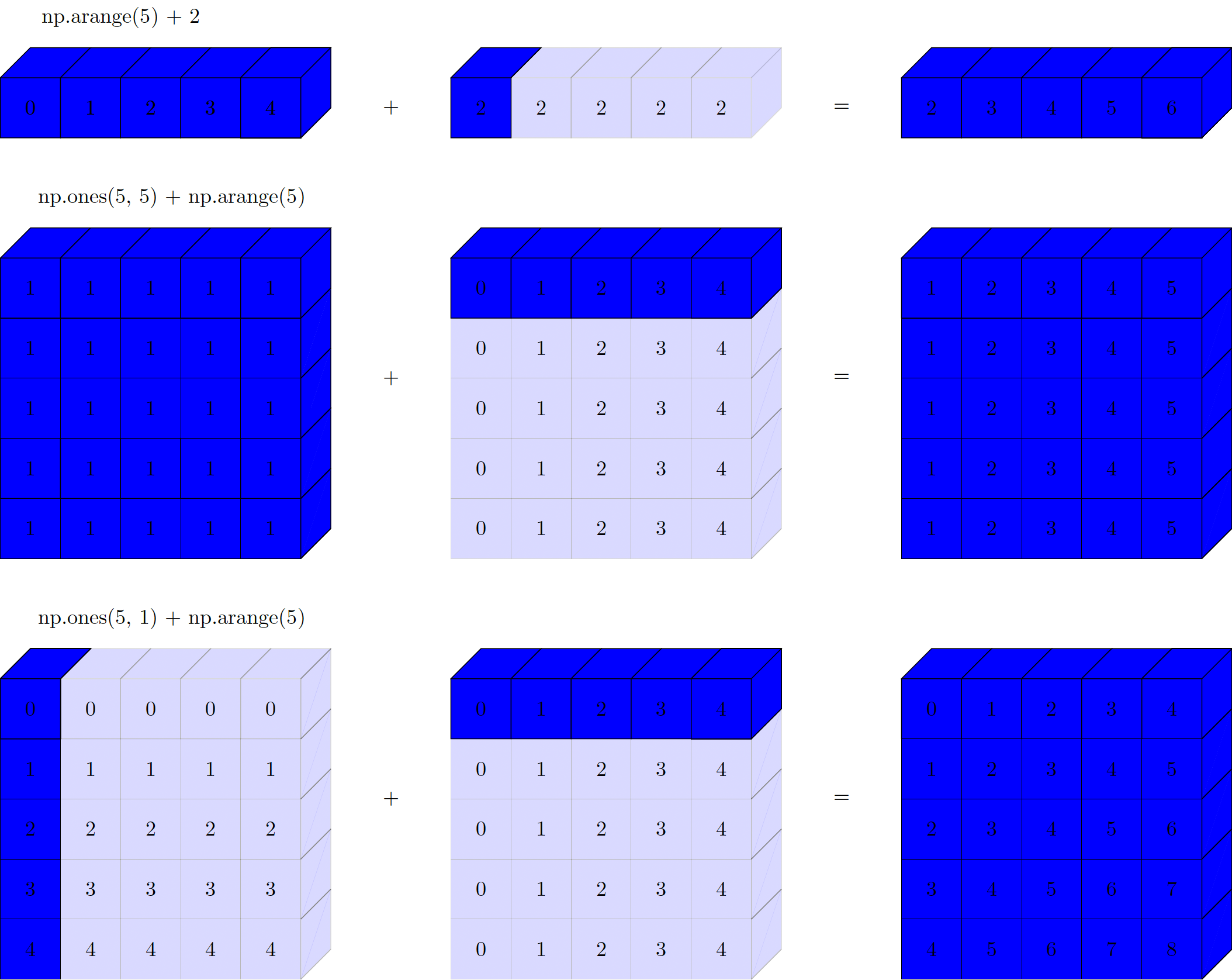
Broadcasting
Broadcasting is NumPy’s powerful mechanism for performing operations on arrays of different shapes.
Intuition
Think of it as “stretching” smaller arrays to match larger ones, enabling element-wise operations without explicit copying.
Broadcasting Rules
- Rule 1 (Padding): Arrays with fewer dimensions are padded with 1s on the left
- Shape (3,) becomes (1, 3)
- Rule 2 (Stretching): Dimensions of size 1 are stretched to match the other array
- Shape (1, 3) can stretch to (4, 3)
- Rule 3 (Compatibility): After rules 1 & 2, shapes must match exactly or error occurs
- (3, 4) and (3, 4) ✓ Compatible
- (3, 4) and (3, 5) ✗ Error!
What is this np.newaxis?
Simply put, numpy.newaxis is used to increase the dimension of the existing array by one more dimension, when used once. Thus:
- 1D array will become 2D array
- 2D array will become 3D array
- 3D array will become 4D array
- 4D array will become 5D array
🤔 Pop Quiz
Can arrays with shapes (3, 1) and (1, 4) be broadcast together?
- Yes, resulting shape will be (3, 4)
- No, incompatible shapes
- Yes, resulting shape will be (3, 1)
- Yes, resulting shape will be (1, 4)
Boolean Masks and Filtering
Idea
Create boolean arrays for filtering and analysis
| Operator | NumPy Function | Description |
|---|---|---|
& |
np.logical_and |
Element-wise AND |
| |
np.logical_or |
Element-wise OR |
~ |
np.logical_not |
Element-wise NOT |
🤔 Pop Quiz
What does arr[arr > 5] return?
- All indices where values are > 5
- A 1D array of all values > 5
- A boolean array
- The count of values > 5
Advanced Indexing
Use arrays of indices to select multiple elements
🤔 Pop Quiz
For array [10, 20, 30, 40, 50], what does arr[[0, 2, 4]] return?
- An error
- array([10, 30, 50])
- array([0, 2, 4])
- array([10, 20, 30])
Sorting Arrays
Efficiency Tip
When you only need the k smallest/largest elements, use partition instead of full sorting. It’s O(n) vs O(n log n)!
NaN-Safe Operations
Common problem: Data that contains missing values
Standard NumPy functions propagate NaN values, potentially ruining calculations. Use NaN-safe versions when dealing with missing data!
| Standard Function | NaN-safe Version | Description |
|---|---|---|
np.sum |
np.nansum |
Sum ignoring NaNs |
np.mean |
np.nanmean |
Mean ignoring NaNs |
np.std |
np.nanstd |
Std deviation ignoring NaNs |
np.var |
np.nanvar |
Variance ignoring NaNs |
np.min |
np.nanmin |
Minimum ignoring NaNs |
np.max |
np.nanmax |
Maximum ignoring NaNs |
np.argmin |
np.nanargmin |
Index of min ignoring NaNs |
np.argmax |
np.nanargmax |
Index of max ignoring NaNs |
np.percentile |
np.nanpercentile |
Percentile ignoring NaNs |
np.median |
np.nanmedian |
Median ignoring NaNs |
🤔 Pop Quiz
What does np.nanmean([1, 2, np.nan, 4]) return?
- NaN
- An error
- 2.333… (mean of 1, 2, 4)
- 1.75 (treating NaN as 0)
Key Takeaways
NumPy arrays are the foundation of numerical computing in Python
Vectorization eliminates loops and speeds up calculations 10-100x
Broadcasting enables flexible operations on different-shaped arrays
Boolean indexing provides powerful data filtering capabilities
Aggregations along axes enable sophisticated data analysis
Integration with pandas, matplotlib, and scikit-learn creates complete workflow
One line takeaway
If you had to take away just one thing from this lecture, it would be: NumPy is not just about arrays, it’s about thinking in terms of vectorized operations and efficient numerical computing patterns that scale to real-world actuarial problems.
- See NumPy lecture notes for detailed explanations and more examples.
- There are two (concrete) examples of counting rainy days in Lausanne and Swedish Automobile claims.
Questions?
DSAS 2025 | HEC Lausanne